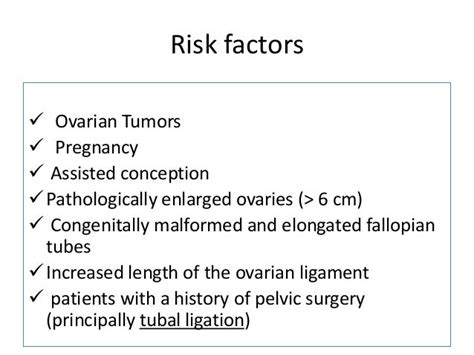
ovarian torsion diagnostic test|risk factors for ovarian torsion : broker The definitive diagnosis of ovarian torsion is made by direct visualization of a rotated ovary during surgery. For this reason, if clinical suspicion remains high with . 21 de fev. de 2024 · El Club Deportivo Oriente Petrolero más conocido como Oriente Petrolero, es un club de fútbol de la ciudad de Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Bolivia, que compite en la Primera División de Bolivia. Fue .
{plog:ftitle_list}
web25 de ago. de 2023 · Download. Sonic the Hedgehog Classic is a fan game by Hez. It began as an offshoot of his earlier fan game Sonic 1 PC, with a variety of new levels. The game .
The only way to get a definitive diagnosis, though, is for a surgeon to see the twisted ovary inside your body. Often, they use a procedure called laparoscopy to examine your ovaries directly. If they see ovarian torsion during the laparoscopy, they can treat it right away . The definitive diagnosis of ovarian torsion is made by direct visualization of a rotated ovary during surgery. For this reason, if clinical suspicion remains high with .
Diagnosis – A definitive diagnosis of ovarian torsion is made by direct visualization of a rotated ovary at the time of surgical evaluation. A presumptive diagnosis of . Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary (and/or fallopian tube) on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary. . Ovarian torsion is a surgical emergency. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function where this is clinically appropriate and it is important to .
A pelvic ultrasound is the best imaging test to diagnose ovarian torsion. If the pelvic ultrasound does not definitively show ovarian torsion but the healthcare provider is still worried about it, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) . Ovarian torsion is a gynaecological emergency: a delay in diagnosis and referral can lead to a reduction in fertility. Ovarian masses are the most common cause of ovarian torsion, but torsion can occur in their absence, .
Diagnosis can be difficult and is mainly based on clinical symptoms and imaging techniques such as ultrasound and MRI. A normal ultrasound scan does not exclude adnexal .
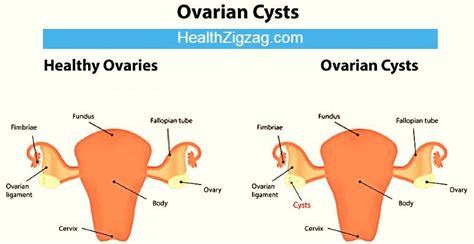
Definitions. ovary fallopian tube ligaments. tubo-ovarian. Etiology. Ovarian enlargement is the most important risk factor. Ovarian cysts, especially: [2] > 5 cm. Dermoid cysts teratoma. .Ovarian torsion - Knowledge @ AMBOSS provides information on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of ovarian torsion. OBJECTIVE. The CT and MRI features of ovarian torsion are illustrated with gross pathologic correlation. Ovarian enlargement with or without an underlying mass is the finding most frequently associated with torsion, but .
The differential diagnosis is broad, based on the patient's age and pregnancy status and gynecologic vs. nongynecologic etiology. . ruptured ovarian cyst, adnexal torsion, and pelvic .
A pelvic ultrasound is the best imaging test to diagnose ovarian torsion. If the pelvic ultrasound does not definitively show ovarian torsion but the healthcare provider is still worried about it, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the abdomen and pelvis might help determine a diagnosis. OBJECTIVE. The CT and MRI features of ovarian torsion are illustrated with gross pathologic correlation. Ovarian enlargement with or without an underlying mass is the finding most frequently associated with torsion, but it is nonspecific. A twisted pedicle, although not often detected on imaging, is pathognomonic when seen. Subacute ovarian hemorrhage . The serum β–human chorionic gonadotropin test result was negative for pregnancy, and urinalysis testing showed no leukocyte esterase or nitrites. MRI of the pelvis was performed to evaluate the worsening pain. . Ovarian torsion: diagnostic features on CT and MRI with pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2012;198(2):W122–W131 .Yaman C, Ebner T, Jesacher K. Three-dimensional power Doppler in the diagnosis of ovarian torsion. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2002 Nov;20(5):513-5. 52. Lee EJ, Kwon HC, Joo HJ, et al. Diagnosis of ovarian torsion with color Doppler sonography: depiction of twisted vascular pedicle. J Ultrasound Med. 1998 Feb;17(2):83-9. 53.
A positive pregnancy test does not eliminate the diagnosis of ovarian torsion, especially early in pregnancy, as a corpus luteum cyst may be the source of torsion. Physical exam should include an abdominal exam and a pelvic exam, including a bimanual exam, to assess for adnexal tenderness and fullness that may be present.
A key diagnostic test is pelvic ultrasonography, which may help demonstrate an asymmetric enlarged ovary with peripherally displaced follicles. In the pediatric population, ovarian torsion may occur in a normal ovary. . What is Known: • Ovarian torsion is a rare diagnosis in the pediatric population. • Aspecific symptoms and differential . Your doctor might also test your blood for tumor markers that indicate ovarian cancer. For example, a cancer antigen (CA) 125 test can detect a protein that's often found on the surface of ovarian cancer cells. These tests can't tell your doctor whether you have cancer, but they may provide clues about your diagnosis and prognosis. Surgery.This leaflet is to help you understand what an Ovarian torsion is, what tests you need and the implication of being diagnosed for you and your baby. . Ultrasound is the first line diagnostic test. There are some ultrasound findings that can help in the diagnosis of adnexal torsion. Unfortunately, blood tests are not useful in the diagnosis of .
This leaflet is to help you understand what an Ovarian torsion is, what tests you need and the implication of being diagnosed for you and your baby. . Ultrasound is the first line diagnostic test. There are some ultrasound findings that can help in the diagnosis of adnexal torsion. Unfortunately, blood tests are not useful in the diagnosis of .
Ovarian torsion. Cysts can grow so big that they distort the shape of your ovary, increasing the likelihood that it’ll twist. The twisting can prevent blood flow to your ovary, causing it to die. . Diagnosis and Tests. How is an ovarian cyst diagnosed? Your healthcare provider will first rule out pregnancy as the cause of your symptoms .
The presence of ovarian blood flow on Doppler sonography cannot exclude ovarian torsion and so should not be used to dismiss the diagnosis of torsion in the presence of a suggestive history and clinical examination: seek a senior gynaecological opinion to determine the need for a diagnostic laparoscopyA key diagnostic test is pelvic ultrasonography, which may help demonstrate an asymmetric enlarged ovary with peripherally displaced follicles. In the pediatric population, ovarian torsion may occur in . consultation before having a diagnosis of ovarian torsion made. This percentage increases to 69% in premenarchal girls. These numbers may . Adnexal torsion is the twisting of the ovary, and often of the fallopian tube, on its ligamental supports, resulting in vascular compromise and ovarian infarction. The definitive management is surgical detorsion, and .
A key diagnostic test is pelvic ultrasonography, which may help demonstrate an asymmetric enlarged ovary with peripherally displaced follicles. In the pediatric population, ovarian torsion may occur in a normal ovary. However, underlying lesions can be found in half of cases. . • Ovarian torsion is a rare diagnosis in the pediatric population. Ovarian torsion is defined as partial or complete rotation of the ovarian vascular pedicle and causes obstruction to venous outflow and arterial inflow. Ovarian torsion is usually associated with a cyst or tumor, which is typically benign; the most common is mature cystic teratoma. Ultrasonography (US) is the primary imaging modality for evaluation of ovarian . Ovarian torsion occurs when the ovary rotates around its supporting ligaments, twisting and squashing the accompanying blood vessels and lymphatics.The term adnexal torsion is preferred because a portion of the fallopian tube is commonly torsed along with the ovary.The term adnexal torsion also encompasses rarer entities that do not affect the ovaries .
Pelvic adnexal torsion is a collective term referring to twisting of an ovary, fallopian tube, or paraovarian cyst on its axis with varying degrees of vascular compromise. Although it is the fifth most common gynecologic emergency, the diagnosis is challenging and often missed due to symptoms, physical examination findings, and imaging features that are nonspecific. . Clinical history is vital in the diagnosis of an adnexal mass (). 4 Risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. The patient's reproductive status and contraception method must be determined . An update on the diagnosis and management of ovarian torsion. Georgios Christopoulos MRCOG, Georgios Christopoulos MRCOG. Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK. Search for more papers by this author. Tony Kelly MRCOG, Tony Kelly MRCOG. Royal Sussex County Hospital, Brighton, UK.
twisted or ruptured ovarian cyst
The adnexa is a set of structures adjacent to the uterus, consisting of the ovaries and fallopian tubes. Even though the fallopian tubes are one of the major adnexal structures, this article will focus on the ovaries and the different types of cysts that can form within the ovary. The ovaries are suspended laterally to the uterus via the utero-ovarian ligament, covered by the .
Ovarian torsion (adnexal torsion) is an infrequent but significant cause of acute lower abdominal pain in women. This condition is usually associated with reduced venous return from the ovary as a result of stromal edema, internal hemorrhage, hyperstimulation, or a mass. Problem Description. Abdominal pain is one of the most common presenting complaints in the pediatric emergency department (ED) with a broad differential diagnosis. 1 An important consideration in children with ovaries is ovarian or adnexal torsion, a time-sensitive surgical emergency. Transabdominal pelvic ultrasound with Doppler (TPUS) is the diagnostic . Magnetic resonance imaging could offer improved specificity to investigate complex ovarian morphology, but more evidence is needed. Tweetable abstract. To investigate adnexal torsion, ultrasound is a good first-line diagnostic test with a pooled sensitivity of 0.79 and specificity of 0.76.
Pregnancy test: Pregnancy is an ovarian torsion risk factor, so it is useful to confirm it or rule it out. Doppler ultrasound: . However, surgical evaluation is the most definitive diagnostic tool for ovarian torsion. Summary. Ovarian torsion is the twisting of an ovary around the ligaments that support it. It is an emergency that requires .
Single Yarn Strength Tester purchase
Yarn Strength Tester purchase
WEBData de Nascimento. Perdi meu protocolo Login. keyboard_arrow_up
ovarian torsion diagnostic test|risk factors for ovarian torsion